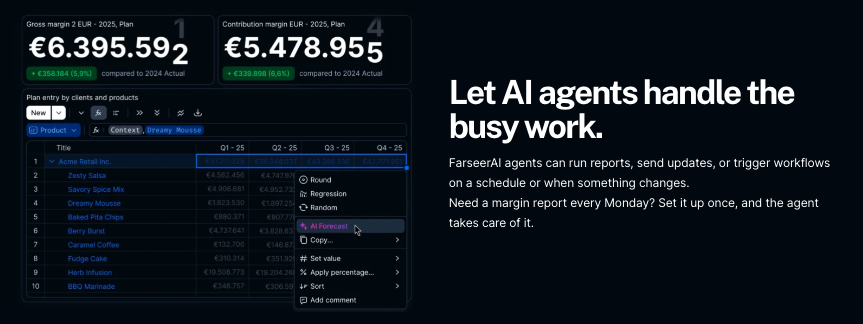
AI trends in FP&A software have moved from abstract discussion to tangible results. Planning cycles run faster, models remain stable for longer, and the volume of routine work handled manually each month continues to decline. What still lags behind is the way the market talks about these shifts. Much of the commentary treats AI as a single concept, even though forecasting, reporting, and modelling each require different forms of intelligence and control.
FP&A teams see the distinction every day. The impact shows up in practical, measurable improvements: how quickly a baseline forecast appears, how scenarios adjust when conditions change, and how much consolidation work disappears from the monthly routine. The real question for finance leaders is no longer whether AI will influence FP&A, but where it delivers value without disrupting governance, accuracy, or existing planning structures.
Read: Finance Automation in 2025: Tools, Use Cases, and Real-World Strategy
This article outlines the AI trends shaping FP&A software in 2026, focusing on the areas where the technology has matured enough to improve accuracy, speed, and decision-making.
Why AI in FP&A Software Is Entering a Practical Phase
FP&A teams are moving away from spreadsheet-heavy cycles and toward structured, model-driven planning. AI is now embedded directly into daily workflows, supporting tasks such as forecasting, reporting, model adjustments, and scenario evaluation. The practical value comes from what AI does inside the FP&A environment: preparing baseline forecasts, generating explanations, updating plans, or triggering recurring workflows.
This is a notable shift from the broader conversation around AI in finance, where the emphasis often remains on generic use cases or standalone chatbots. In FP&A, the real change appears in the core planning processes where accuracy, consistency, and control matter most. As a result, AI has become a functional extension of the planning model rather than a separate analytical layer.
Read more: Will AI Replace Finance Jobs? Here’s What’s Actually Happening
Trend 1: AI-Generated Baseline Forecasts Become Standard
AI-generated baselines are becoming the natural starting point for forecasting. Instead of rebuilding models or stitching inputs together, teams receive an initial forecast produced directly from historical patterns, operational drivers, and the latest performance signals. The effect is immediate: planning cycles begin faster, and the model moves into an analysable state with minimal preparation.
The human role remains central. Finance teams still review assumptions, adjust key drivers, and add context that algorithms cannot detect. The shift is that the first draft of the forecast appears as soon as data refreshes, allowing analysts to focus on interpretation rather than assembly.
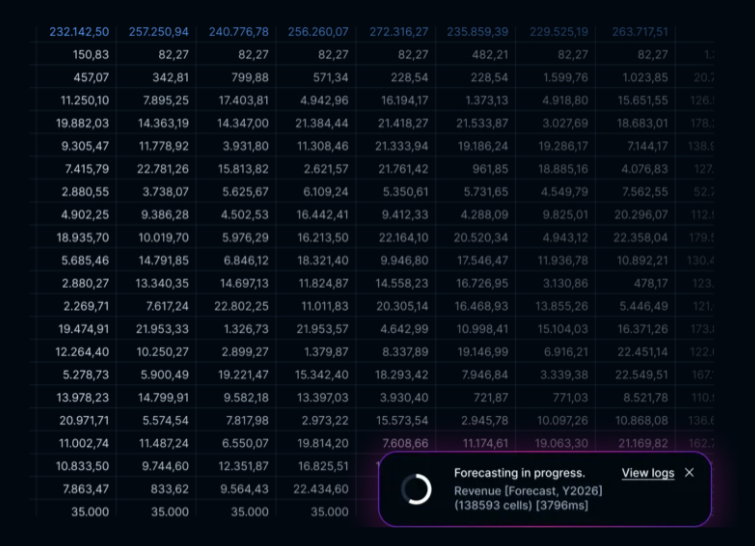
Rolling forecasts gain the most from this evolution. Because the underlying model updates continuously, the AI can generate a new baseline the moment operational, HR, or sales inputs change. Platforms with a structured driver framework and reliable calculation engine make this especially effective, as the AI can read the relationships already defined in the model and apply them consistently.
The result is a more stable, continuous forecasting process where FP&A can react to changes with greater speed, precision, and confidence.
Trend 2: Chat-Based Forecasting and Reporting Become a Daily Habit
Chat-based forecasting is becoming part of the everyday FP&A workflow. Instead of navigating dashboards or assembling filters, analysts now ask direct questions and receive model-backed answers within seconds. Updated forecasts, variance explanations, and short summaries are delivered in plain language, generated from the same structured logic that drives the planning model.
Some FP&A platforms now extend this directly into the tools teams already use. For example, an FP&A system may provide WhatsApp access to forecasts, variances, and driver updates, allowing users to query the model from a mobile device and receive consistent results powered by the central calculation engine. Because the interaction runs through familiar communication channels, it fits naturally into existing routines and shortens the path from question to answer.
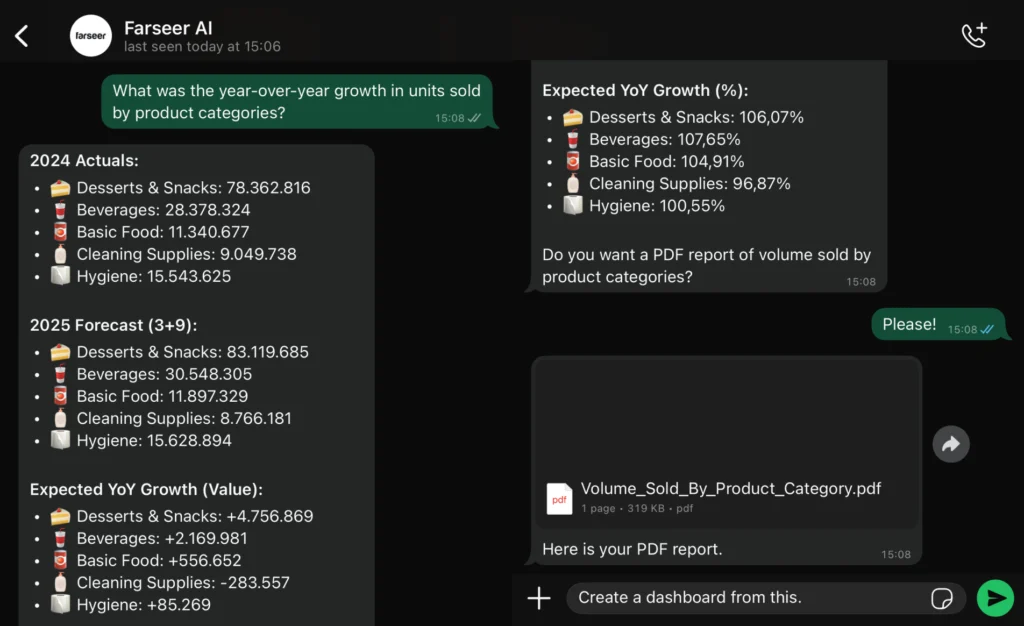
The benefit is immediate: FP&A gains quick clarity without opening the full model, and decision-makers receive timely, model-accurate insights wherever they are.
Trend 3: AI Agents Start Handling Recurring FP&A Work
AI agents are moving into the core of FP&A operations, not as an add-on but as a built-in part of the planning environment. They now manage recurring tasks such as scheduled reports, plan updates, allocations, and routine checks. Because these actions run directly on top of structured model logic, the workflow becomes more predictable and far less dependent on manual supervision.
Event-driven execution
When new data arrives, whether from operations, HR, or sales, agents automatically trigger the relevant updates. This removes the need for constant data pulls or repeated version checks, particularly in organisations where integrations refresh throughout the day.
Shift toward interpretation
As execution moves into the background, FP&A teams focus on reviewing outputs, validating assumptions, and advising stakeholders. Agents become a quiet operational layer that keeps the model current while the finance team directs attention to analysis, communication, and forward planning.
Trend 4: Variance Explanations and Performance Narratives Become Automatic
The narrative layer is finally catching up with the numbers. AI now generates variance explanations, driver breakdowns, and short performance summaries directly from the model. What used to require hours of manual writing becomes available the moment data refreshes.
A quick comparison shows how sharp the shift is:

This is especially valuable in monthly consolidation, budget vs. actual reviews, and rolling forecast updates, where the same narrative often needs to be recreated repeatedly.
With the narrative automated, FP&A moves faster and spends its time on decisions, not rewriting explanations.
Trend 5: Real-Time Scenario Planning Guided by AI
Scenario planning is no longer a manual exercise where teams build versions from scratch. AI now acts as a silent strategist, surfacing relevant what-ifs the moment underlying conditions shift.
The process looks increasingly like this:
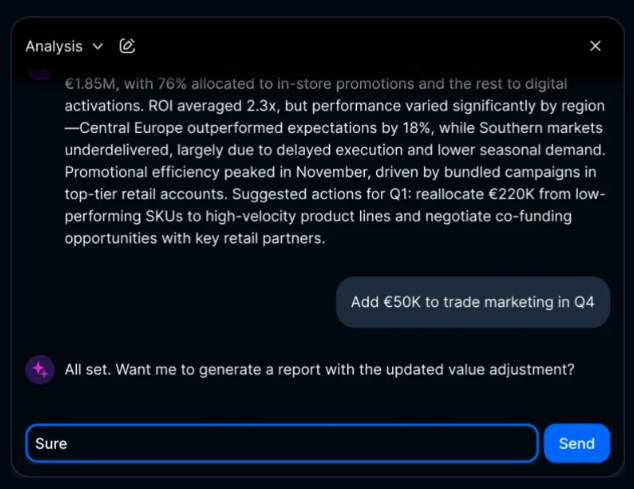
In some platforms, this runs directly inside the same modelling environment, AI adjusts the drivers, generates the scenario, updates downstream statements, and logs the version without requiring separate files or manual stitching.
This keeps forecasts aligned with real operational signals and reduces the time needed to explore options during volatile periods.
Trend 6: AI Learns From the Company’s Own Models, Not Generic Data
AI in FP&A is becoming model-aware. Instead of relying on generic datasets or one-size-fits-all prediction methods, modern systems now learn directly from the organisation’s driver-based forecasting structure. They read the model’s logic, understand how drivers connect to outputs, and apply the appropriate forecasting method to each metric.
The outcome is straightforward: AI becomes a collaborator inside the workflow. It adapts to the company’s model rather than forcing a new one, ensuring that every forecast, adjustment, or scenario remains aligned with established assumptions and the underlying driver logic.
Trend 7: FP&A Software Moves Toward Fully Connected Planning
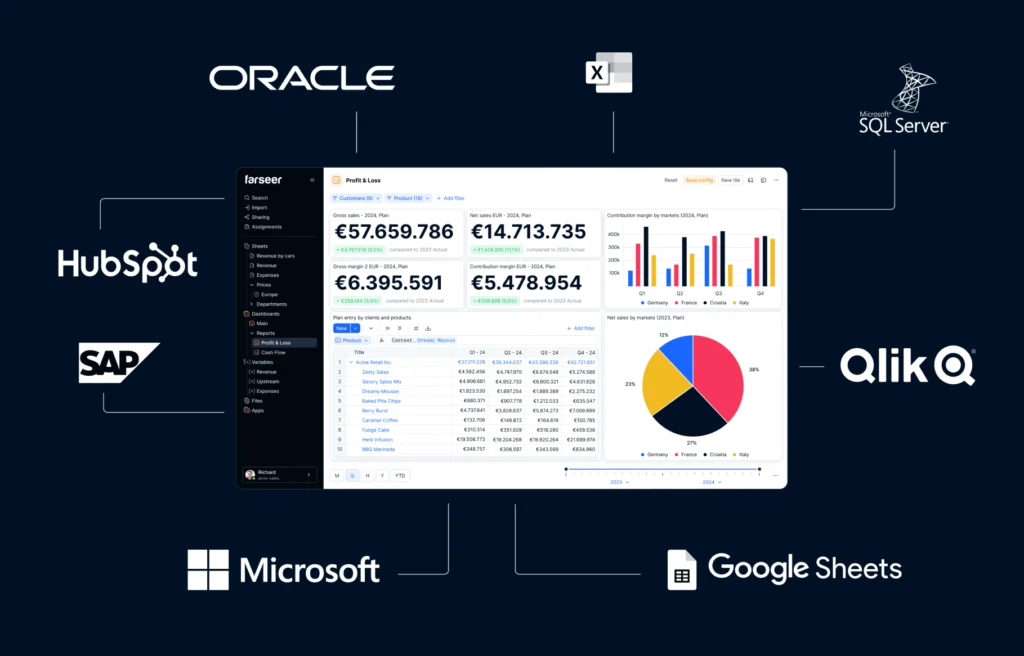
AI in FP&A depends heavily on the integrity of the environment it operates in. When data is scattered across spreadsheets, shared folders, and departmental files, even the strongest algorithms struggle to produce consistent results. This is why modern FP&A software is moving toward fully connected planning, a structure where finance, HR, sales, and operations contribute to a single model.
In a connected environment, AI can finally deliver stable outputs. Workforce assumptions flow directly into cost plans, revenue models reflect operational constraints, and consolidation logic applies uniformly across the organisation.
Instead of stitching numbers together at month-end, the system integrates everything upfront through structured modelling and secure, automated data flows.
Read more: The State of Finance – Financial Industry Trends and Predictions for 2026
What Finance Teams Should Prioritize When Evaluating AI in FP&A Software
When assessing AI capabilities, finance teams should focus on practical criteria that determine whether the technology can support real planning workloads:
- The AI must operate inside the planning model, using existing structures and drivers rather than external logic.
- Forecasting outputs should be explainable, with clear reasoning behind the projections.
- AI-generated reporting needs to be ready for distribution, not partial drafts that require extensive manual editing.
- Agents should automate genuine FP&A workflows such as updates, allocations, reviews, or scheduled tasks.
- Results must align with the company’s drivers, versioning rules, and modelling structure to avoid inconsistencies across plans and scenarios.
This checklist helps teams distinguish between marketing promises and software that can genuinely support day-to-day FP&A operations.
Conclusion
AI is reshaping FP&A, but its impact depends entirely on the strength of the underlying planning environment. AI speeds up forecasting, highlights patterns earlier, and removes a meaningful portion of repetitive work. What it cannot replace is the judgment required to set assumptions, challenge results, and communicate implications to leadership.
The teams that will gain the most are those willing to adjust their routines, shorten their cycles, and rely more heavily on structured models rather than isolated spreadsheets. When processes are clear and the planning model is stable, AI becomes a natural extension of the workflow. The outcome is a more responsive FP&A function, one that moves with the business instead of reacting to it, and one that can provide leadership with timely, well-supported insights.